Wołosz D., Mazurek-Budzyńska M., Rajewska P., Musiatowicz M., Milanowska M.W., Gołofit T., Kędzierski M., Deshmukh S., Brüll R., Parzuchowski P.G.
Toward a circular economy: Upcycling PET and fatty diamine derivatives into recyclable non–isocyanate poly(ester-urethane)s
European Polymer Journal 2025, 239,114330
DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2025.114330
Abstract
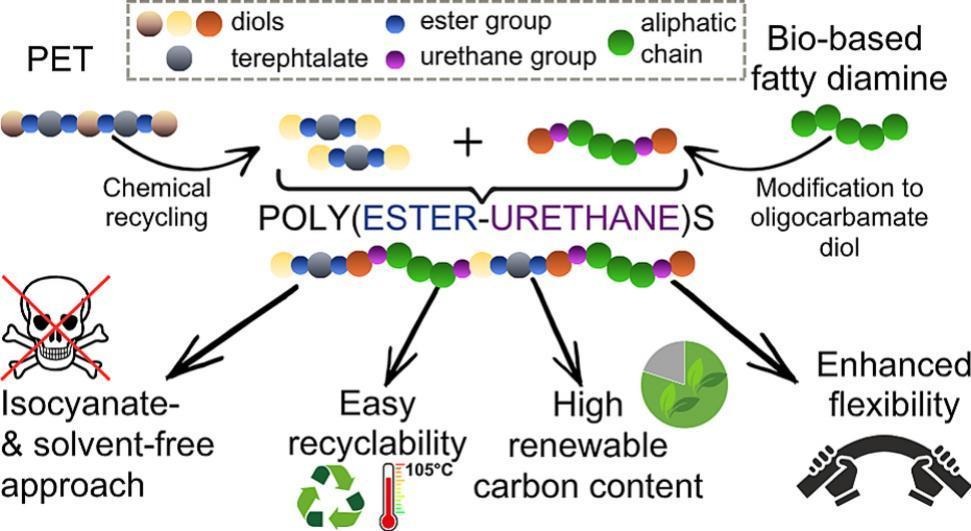
Meeting the criteria of renewability and recyclability poses a relevant challenge to develop circular polyurethanes with sustainable lifecycles. Although conventional poly(ester-urethane)s and their non–isocyanate counterparts (NIPEUs) were synthesized from recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET), they typically lack renewable content and circularity. Hence, this work addressed the preparation of circular NIPEU of high renewable content and mechanical integrity after multiple reprocessing tests. The ester-urethane copolymers were obtained by combining recycled PET-based aromatic poly(pentamethylene terephthalate) diol (PET_PD) with fatty diamine-based carbamate diol (PRI_HD), incorporating a 58–78 wt% total renewable content. The polymers structure was proven by FT-IR and NMR spectroscopy, while significant molar mass growth, accompanying the melt polycondensation synthesis, was evidenced by SEC analysis (Mn= 19,000–30,400 g·mol−1). Thermal and mechanical behavior were adjusted by varying the molar ratio of aromatic ester to aliphatic urethane moieties. PET_PD segments provided stiffness, mechanical strength, thermal stability, and crystallinity whereas PRI_HD ones increased flexibility and amorphousness. Semi-crystalline NIPEUs exhibited the most favorable mechanical performance, while amorphous ones were less tough and more flexible. Crucially, the mechanical properties durability was observed after three consecutive low-temperature reprocessing tests (105 °C), demonstrating potential for closed–loop material lifecycle and reduced plastic waste generation.
Pöttgen S., Mazurek-Budzyńska M., Wischke C.
The role of porosity in polyester microparticles for drug delivery
Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 672, 125340.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125340
Abstract
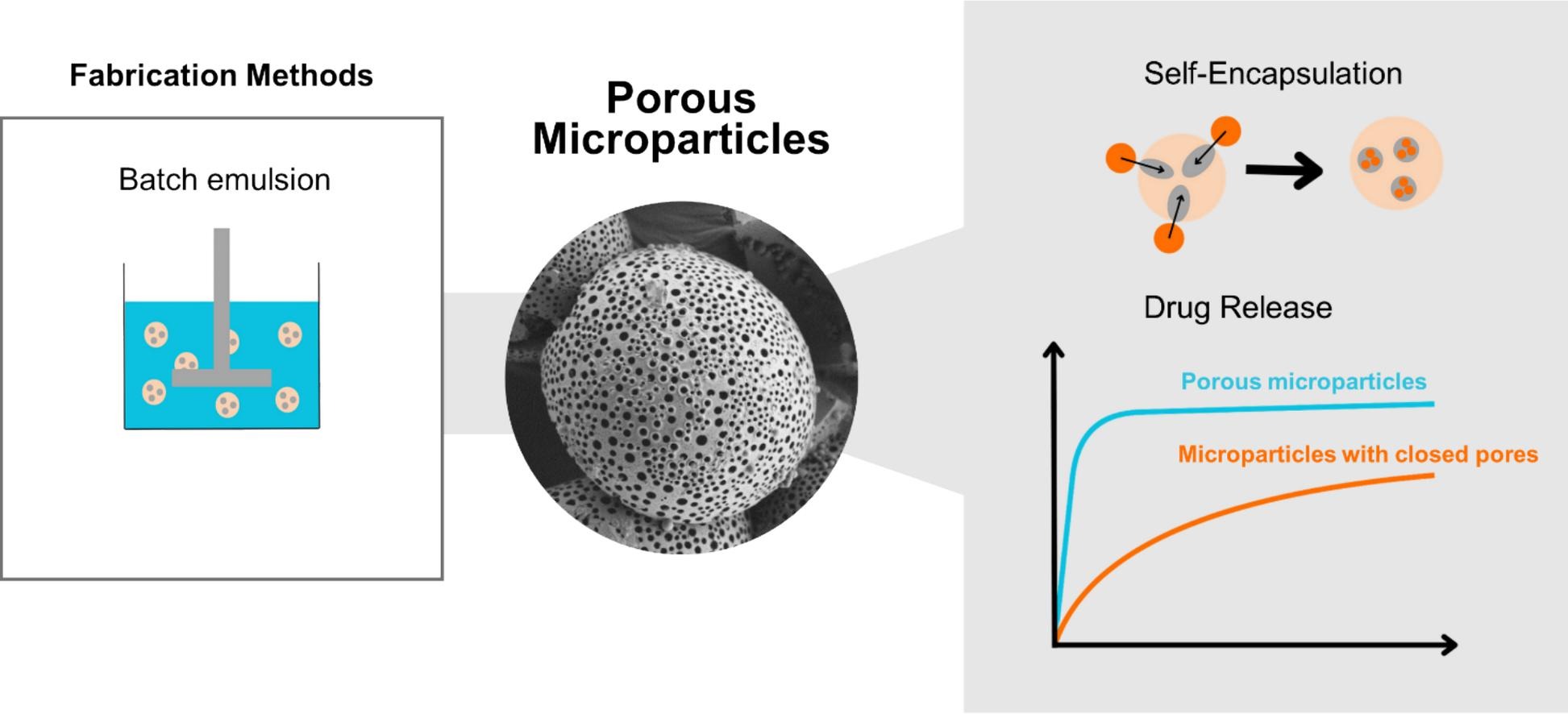
Polymer microparticles are a cornerstone in the field of injectable sustained delivery systems: They allow the entrapment of various types of hydrophobic or hydrophilic drugs including biopharmaceuticals. Microparticles can be prepared from the material of choice and tailored to specific target sizes. Importantly, they can retain the drug at the local administration site to achieve a sustained drug release for long-term therapeutic effects. This review focuses on the role of porosity of microparticles as a tremendously important property. Principles to prepare porous carriers via different techniques and additives are discussed, emphasizing that porosity is not a static property but can be dynamic, e.g., for particles from polylactide or poly(lactide-co-glycolide). Considering the contribution of porosity in the overall assessment of drug carrier systems, as well as their manipulation/alteration post-production such as by pore closing, will enlarge the understanding of polymer microparticles as an important class of modern pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Thamer I., Mazurek-Budzyńska M., Kumaravel, K.
Sustainable biopolymer design: Extraction of chitin and chitosan using natural deep eutectic solvents with improved antibacterial features
Materials & Design 2025, 259, 114775.
DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2025.114775
Abstract
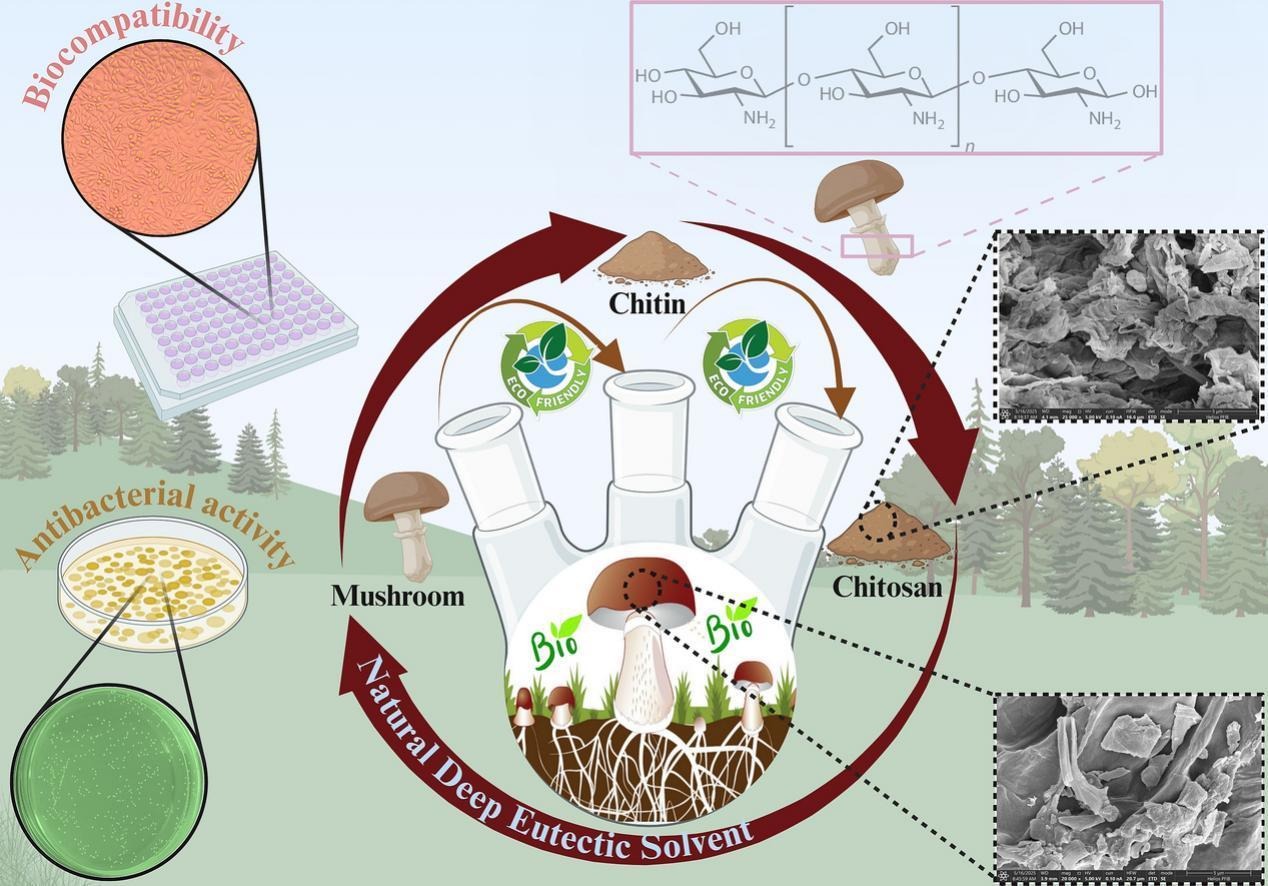
The extraction of biopolymers using natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) offers a promising approach for developing sustainable and biocompatible materials for biomedical applications. In this study, a novel and environmentally friendly process has been developed for extracting chitin and chitosan from organic Agaricus bisporus (A. bisporus) mushrooms, which serves as a readily available and renewable resource. NADES not only enhances the extraction efficiency but also preserves the structural integrity of the biopolymers. The characteristics of these biopolymers were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermogravimetric (DTG/TGA) analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) techniques. By optimizing the NADES extraction conditions, high-purity chitin (98.58 %) and chitosan (98.69 %) were achieved, surpassing the purity levels achieved by traditional chemical methods. NADES-extracted chitosan exhibited a remarkable degree of deacetylation (DD) of up to 94.22 %, and a crystallinity index (CrI) of up to 61.77 %, highlighting its enhanced functionality for biomedical applications. Moreover, the NADES-derived biopolymers showed excellent biocompatibility with L929 fibroblast cells. They exhibited dose-dependent antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) and exhibited promising antioxidant and biodegradability properties.
Wołosz D., Fage A.M., Parzuchowski P.G., Świderska A., Brüll R., Elsner P.
Sustainable associative thickeners based on hydrophobically modified ethoxylated poly(hydroxy-urethane)s end-capped by long alkyl chains
Progress in Organic Coatings 2023, 179, 107514
DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2023.107514
Abstract
Rolińska K., Bakhshi H., Balk M., Parzuchowski P., Mazurek-Budzyńska M.
Influence of the hard segments content on the properties of electrospun aliphatic poly(carbonate-urethane-urea)s
RSC Advances 2024, 14, 15766-15775
DOI: 10.1039/D4RA01726A
Abstract
Wołosz D., Mazurek-Budzyńska M., Rolińska K., Fage A.M., Zimny A., Dębowski M., Gołofit T., Węgrzyk G., Ryszkowska J., Parzuchowski P.G.
Sustainable and CO2-rich electrospun nonwovens with enhanced mechanical properties obtained from isocyanate-free aliphatic-aromatic poly(carbonate-urethane)s
Polymer 2024, 311, 127509
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2024.127509
Abstract
Rolińska K., Bakhshi H., Balk M., Blocki A., Panwar A., Puchalski M., Wojasiński M., Mazurek-Budzyńska M.
Electrospun Poly(carbonate-urea-urethane)s Nonwovens with Shape-Memory Properties as a Potential Biomaterial
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering 2023, 9, 6683-6697
DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c01214
Abstract
Razzaq, M.Y., Balk, M., Mazurek-Budzyńska, M., Schadewald, A.
From Nature to Technology: Exploring Bioinspired Polymer Actuators via Electrospinning
Polymers, 2023, 15, 4029
DOI: 10.3390/polym15194029
Abstract
Dziekan Z., Pituła E., Kwietniewski N., Stonio B., Janik M., Śmiarowski T., Koba M., Parzuchowski P., Niedziółka-Jönsson J., Śmietana M.
Performance of nanoimprinted and nanocoated optical label-free biosensor – nanocoating properties perspective
Optics and Lasers in Engineering 2022, 153, 107009
DOI: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2022.107009
Abstract
Wołosz D., Parzuchowski P.G., Rolińska K.
Environmentally Friendly Synthesis of Urea-Free Poly(carbonate-urethane) Elastomers
Macromolecules 2022, 55, 4995–5008
DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.2c00706
Abstract
Wojciechowski C., Mazurek-Budzyńska M., Palinska A., Chwojnowski A., Granicka L., Sikorska W., Rokicki G.
Preparation and characterization of partially degradable hollow fiber membranes based on polysulfone/poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide-co-ε-caprolactone) blends
Desalination and Water Treatment 2020, 202, 38-47
DOI: 10.5004/dwt.2020.26154
Abstract
Behl M., Razzaq M.Y., Mazurek-Budzyńska M., Lendlein A.
Polyetheresterurethane Based Porous Scaffolds with Tailorable Architectures by Supercritical CO2 Foaming
MRS Advances 2020,
DOI: 10.1557/adv.2020.345
Abstract
Wołosz D., Parzuchowski P.G.
Biobased non-isocyanate poly(carbonate-urethane)s of exceptional strength and flexibility
Polymer 2022, 254, 125026
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2022.125026
Abstract
Zalewski M.J., Mamiński M.Ł., Parzuchowski P.G.
Synthesis of Polyhydroxyurethanes—Experimental Verification of the Box–Behnken Optimization Model
Polymers 2022, 14, 4510
DOI: 10.3390/polym14214510
Abstract
Dominik Wołosz, Paweł G. Parzuchowski, Aleksandra Świderska
Synthesis and characterization of the non-isocyanate poly(carbonate-urethane)s obtained via polycondensation route
European Polymer Journal 2021, 155, 110574
DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2021.110574
Abstract
Aleksandra Świderska, Paweł G. Parzuchowski, Radosław Żurowski, Anna Więcław-Midor, Dominik Wołosz
Energy dissipating poly(hydroxyurethane) elastomers – Synthesis, characterization and comparison with shear thickening fluid materials
Polymer 2021, 230, 124084
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2021.124084
Abstract
Wojciechowski K., Gutarowicz M., Mierzejewska J., Parzuchowski P.
Antimicrobial Films of Poly(2-aminoethyl methacrylate) and Its Copolymers Doped with TiO2 and CaCO3
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110605
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110605
Abstract
Parzuchowski P., Mamiński M.
Poly-(3-ethyl-3-hydroxymethyl)oxetanes—Synthesis and Adhesive Interactions with Polar Substrates
Polymers 2020, 12, 222
DOI: 10.3390/polym12010222
Abstract
Parzuchowski P.G., Świderska A., Roguszewska M., Rolińska K., Wołosz D., Mamiński M.
Hyperbranched Poly(ether-siloxane)s Containing Ammonium Groups: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity
Polymers 2020, 12, 856
DOI: 10.3390/polym12040856
Abstract
Wojciechowski K., Gutarowicz M., Janke K., Jurek I., Kaczorowski M., Mierzejewska J., Parzuchowski P.
Colloidal Stability of Positively Charged Dispersions of Styrene and Acrylic Copolymers in the Presence of TiO2 and CaCO3
Colloids and Interfaces 2019, 3, 20
DOI: 10.3390/colloids3010020